System Architecture
CityScope is composed of a series of tools loosely connected to each other. The tools are developed in different languages and frameworks, and they communicate through a central server, CityIO.
CityScopeJS
CityScopeJS is a modular, open-ended architecture for MIT CityScope project.
- User interface to interact with the CityScope projects
- Uses CityIO Websockets to communicate with the server
- New user experience and design for the CityScope projects
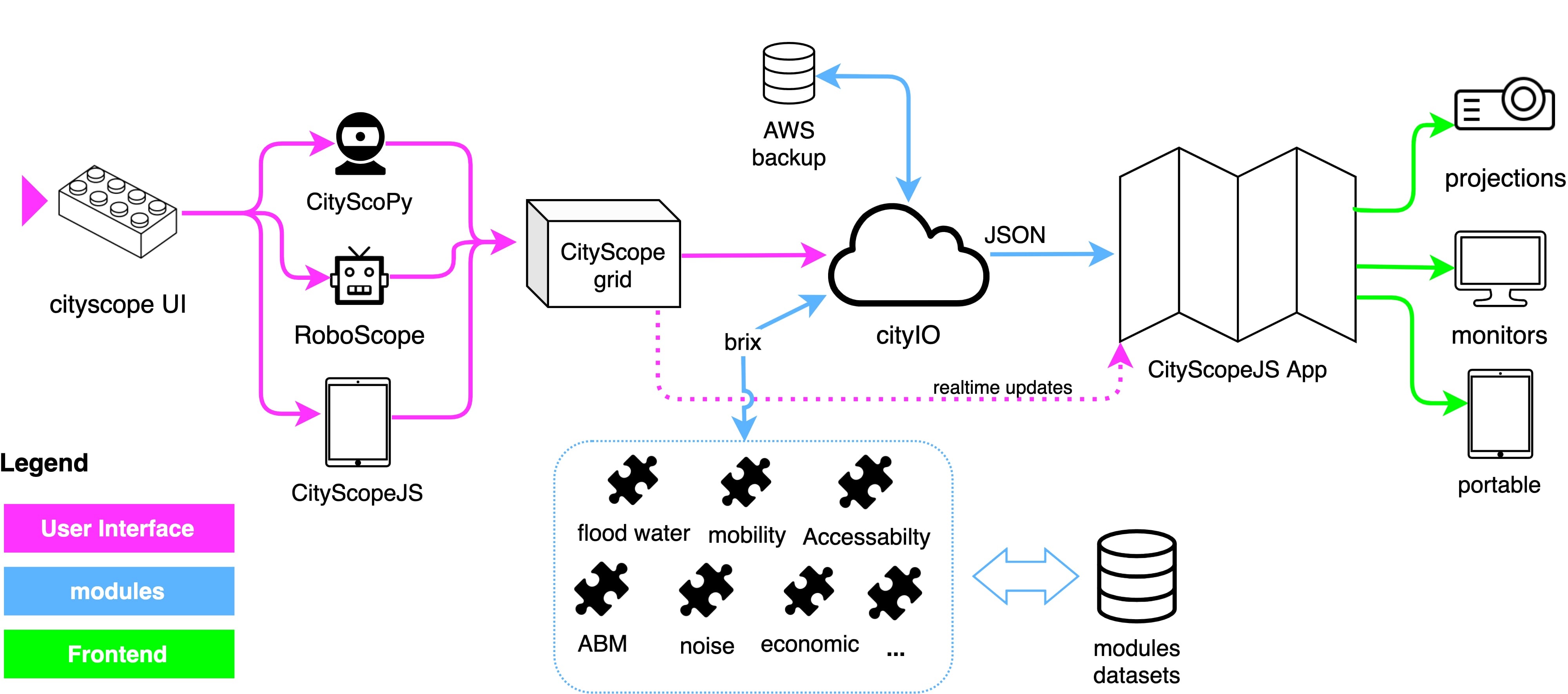
Figure: CityScopeJS Architecture (Photo: Ariel Noyman)
CityScopeJS includes several other modules for building, testing and deploying an end-to-end CityScope platform. Each module is developed as a standalone part of the system with minimal dependency on others. Data flow between modules is done using cityIO, which operates between the different modules.
Modules
Different analysis modules calculate various indicators on urban performance, such as noise, mobility, energy and others. These analysis modules are developed by experts in each evaluation field.
- Urban Indicators module: https://github.com/CityScope/CS_Urban_Indicators
- A service providing mobility simulation, Agent Based Simulation, and aggregated mobility prediction for CityScope projects https://github.com/CityScope/CS_Mobility_Service
- Noise Modeling for Grasbrook, Hamburg: https://github.com/CityScope/CSL_Hamburg_Noise
- Agent Based Modeling https://github.com/CityScope/CS_Simulation_GAMA
- Traffic Simulation module using DLR SUMO https://github.com/CityScope/CS_SUMOscope
CityScope Server (cityIO)
CityIO is a server program that saves tables to have different software (visualization, simulation) read/write information. It exposes an API to serve JSON files representing table info.
- Enables the communication between the different components of the system.
- Saves the projects to access them seamlessly in all the components.
- Rebuilt to allow real-time communication, using WebSockets.
See https://github.com/CityScope/CS_CityIO
Tangible User Interfaces
CityScope also includes tangible user interfaces (TUIs) that allow users to interact with the system in a physical way. These interfaces are developed using the CityScopeJS platform.
- CityScope Scanner: https://github.com/CityScope/CS_CityScoPy